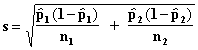These tests are used when the random sample is drawn from a Normal distribution with a known variance.
-
Confidence Interval for m
Confidence Limits
![]()
In this sampling situation the variances of the two populations are known.
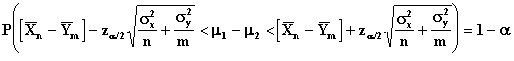
Confidence Limits
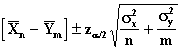
When the sample size is large, the Central Limit Theorem allows us to calculate confidence intervals for any distribution using these formulas (compare these with the ones for proportions in V).
-
Confidence Interval for m
![]()
where 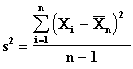
Confidence Limits
![]()
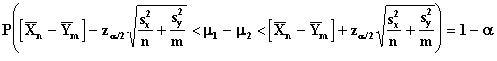
Confidence Limits
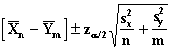
These tests are used when the random sample is drawn from a Normal distribution with unknown variance.
-
Confidence Interval for m
![]()
where 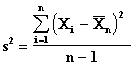
Confidence Limits
![]()
In this sampling situation the variances of the two populations are assumed to be the same.
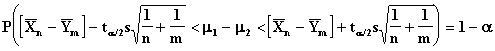
where 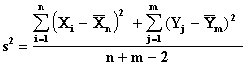
This test is used when the random sample is drawn from a Normal Distribution.
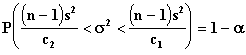
where 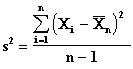
Confidence Limits 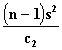 and
and
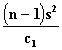
When the sample size is large, the
Central Limit Theorem allows us to
calculate confidence intervals for proportions (technically the random
sample is drawn from a
Bernoulli distribution). Recall
that
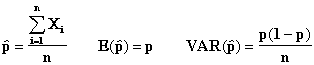
![]()
Using the Central Limit Theorem we assume that
![]() ~
~
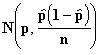
-
Confidence Interval for p
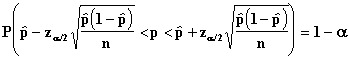
Confidence Limits
![]()
Let p1 and p2 be the two population proportions and let n and m be the sample sizes from the two populations respectively. Using the Central Limit Theorem we assume that
![]() ~
~
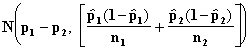
![]()
where